Top 10 Economic Incentive Program Types to Target During the Site Selection Process
by Kelley Rendziperis, on Oct 17, 2023 7:30:00 AM
Editor's Note: This article was originally published in September 2017 and has been revamped and updated with current information.
The pursuit of economic incentives has become ingrained in the site selection process. Economic incentives are offered by public and private governmental and economic development organizations at the federal, state, county and municipal levels. They are pursued for all types of projects including call centers, data centers, distribution centers, headquarters, manufacturing plants, research and design, retail and software development operations. In this blog, Site Selection Group provides a summary of the more commonly used economic incentive programs at the state and local levels.
The following graphic shows state and local economic incentives frequently pursued in relation to a company’s commitment to incremental capital investment and headcount within a community:
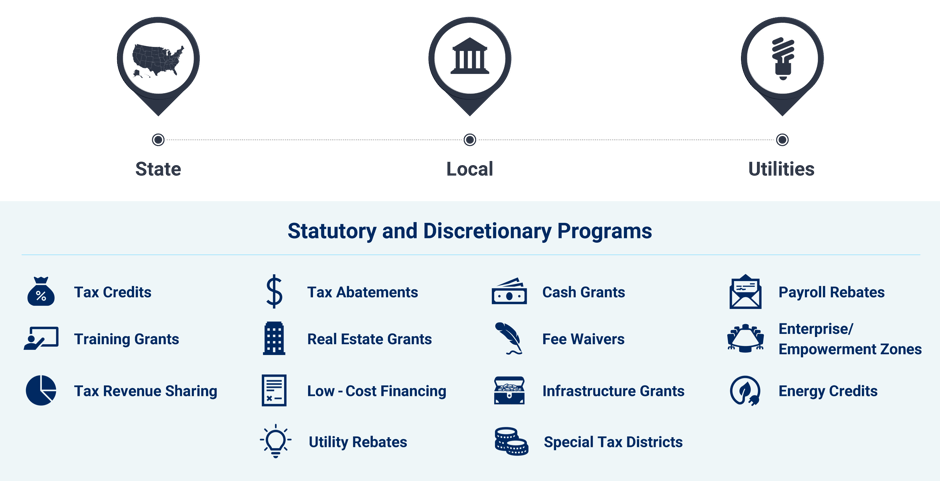
10 frequently used state and local economic incentive programs
Economic incentive programs vary state-to-state, county-to-county and city-to-city; however, there are common categories that most economic incentives programs fall into. To help understand these different categories, we summarized some of the more commonly utilized economic incentive programs throughout the U.S.
1. Tax credits
Tax credits often come in the form of income tax credits based on job creation and/or investment. The most important consideration is to ensure the credit is realizable, and if not, that it is refundable or transferable. Refundable tax credits are ideal because they result in a direct cash benefit to the extent a company does not have liabilities to offset. Transferable credits may be transferred to related entities, and other tax bases within the state, or transferable to third parties and able to be sold on the open market. The goal is to procure a credit you can utilize.
2. Tax rebates
Tax rebates evolved out of a need to solve the problem with unutilized tax credits. Rebates can be based on increased payroll, property tax revenue or sales tax revenues. Another popular rebate is related to energy efficiency improvements. Rebates are a good performance-based tool to incentivize a project.
3. Real and personal property tax abatements
Property tax abatements are one of the most common forms of economic incentives. This incentive can help reduce real and/or personal property taxes on average by 50% and the term varies by location. Some states do not have the ability to grant a property tax abatement outright and thus have mechanisms to offer property tax savings via bond transactions in tandem with payments-in-lieu-of-taxation resulting in the subject property being owned by a governmental entity and thus exempt from taxation.
4. Sales tax benefits
Certain expenditures, such as manufacturing equipment, are statutorily exempt from sales tax in many states. However, some purchases that would otherwise be taxable may qualify for an exemption or reimbursement through negotiation. In addition, if a project generates substantial sales tax revenues, it is possible there may be the ability to enter into a sales tax revenue sharing agreement.
5. Training grants
Training incentives vary by jurisdiction. Some jurisdictions offer in-kind services while others may offer cost offsets to training expenses if participating with a local educational institution. Direct training grants may be awarded in the form of reimbursements, based on either job creation and/or actual training expenses. The compliance process associated with direct training reimbursements can be challenging and it is important to fully understand the process in advance of hiring. Reimbursements can be limited to only the wages of the trainer and development of educational materials, and not to trainee wages. Furthermore, the trainer may need to be provided by a third party and not an internal training resource. Thus, the compliance cost may outweigh the potential benefits.
6. Cash grants and forgivable loans
This type of incentive is favored heavily by companies and can be very valuable especially if you are facing upfront capital investment at your facility for infrastructure, training or other costs such as equipment. For example, in many cities in Texas, companies may be eligible for cash grants for each job created. These will range between $500 to $10,000 per job depending on the city and the wages being paid. The most popular of all incentives are the upfront direct cash payments made to offset initial project costs; however, many communities are now structuring such assistance to be paid out over a longer period based on performance. Loan forgiveness, or reduced financing cost, is another popular tool to convey benefits, subject to meeting project commitments.
7. Utility discounts and rebates
Utility companies may provide discounted utility rates or utility-related infrastructure assistance. These benefits can be very valuable for heavy power users such as data centers and manufacturing plants. In some cases, utilities can provide economic development grants for competitive job creation and capital investment.
8. Real estate and infrastructure grants
There are many communities willing to provide land or a free building in exchange for capital investment and new jobs. The land or building is typically owned by the city or economic development organization. There are even speculative buildings that have been financed and built by economic developers to attract companies whereby they provide a turnkey facility for free rent over the lease term. In addition, infrastructure grants are often used by the community to fund fiber to your building, increased power supply to the site, the addition of roads, and/or ingress/egress to a building.
9. Priority permitting and fee waivers
Projects are typically required to seek permits and often charged fees by cities and counties related to zoning, permitting and other regulatory requirements. You can bypass these delays and expenses through the reduction or waiver of fees, as well as expedite your project to the top of the permitting approval list.
10. Tax-free zones
Some states will eliminate all or a portion of your tax burden by locating and creating jobs in designated geographic areas. These zones may often be in an economically challenged area, so it is important to carefully evaluate labor conditions. A good example of a tax-free zone is Pennsylvania’s Keystone Opportunity Zones, which eliminates most state and local taxes within underdeveloped areas.
Conclusion
Economic incentives in the site selection process continue to play a critical role and have become an expectation by business owners. When securing an economic incentive package, it is important to accurately value the benefits and determine the realizability of each incentive. If a particular benefit is not applicable to the particular business operations, then a company should evaluate whether it can shift those benefits to another category.
